AWS Prompting Techniques
Fundamentals of Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is an emerging field that focuses on developing, designing, and optimizing prompts to improve the output of LLMs for your needs.
With prompt engineering, you can guide the model's behavior to achieve the outcomes you want.
Prompt Engineering vs Fine-Tuning
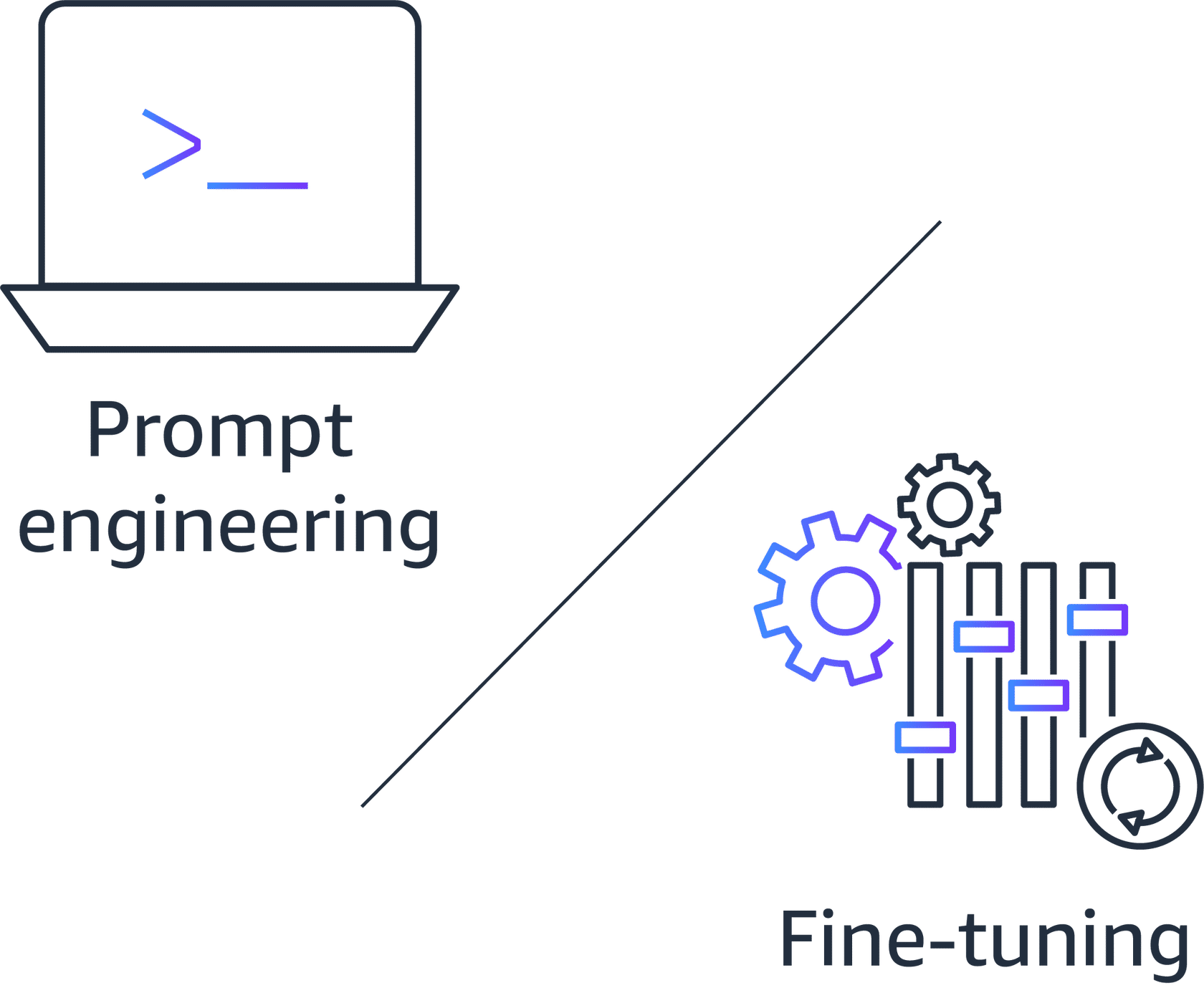
Prompt engineering differs from fine-tuning.
When fine-tuning, you adjust the weights or parameters using training data to optimize a cost function.
Fine-tuning can be an expensive process, both in computation time and cost.
With prompt engineering, you guide the trained foundation model (FM), large language model (LLM), or text-to-image model to provide more relevant and accurate answers.
LLM Interactions
Prompt engineering is the fastest way to harness the power of large language models.
By interacting with an LLM through a series of questions, statements, or instructions, you can adjust LLM output behavior based on the specific context of the output you want to achieve.
Effective prompt techniques can help your business accomplish the following benefits:
- Boost a model's abilities and improve safety.
- Augment the model with domain knowledge and external tools without changing model parameters or fine-tuning.
- Interact with language models to grasp their full capabilities.
- Achieve better quality outputs through better quality inputs.
Elements of a prompt
A prompt's form depends on the task. Prompts can contain some or all of the following elements:
Task description or how to perform it
Information to guide the model
The input for which you want a response
The output type or format
Example prompt breakdown
Store: Online, Service: Shipping.
Review: Amazon Prime Student is a great option for students looking to save money. Not paying for shipping is the biggest save in my opinion. As a working mom of three who is also a student, it saves me tons of time with free 2-day shipping...
Design effective prompts
Carefully design your prompts for the best output. Each tip below includes examples comparing less effective and more effective prompts:
1. Be clear and concise
Use straightforward, natural language. Avoid ambiguity and isolated keywords.
2. Include context
Provide details that help the model respond accurately—type of business, intended use, etc.
3. Specify the response format
State the format (summary, list, poem), length, style, or content requirements clearly.
4. Mention desired output at the end
State what response you want at the end to keep the model focused.
5. Start with a question
Use who, what, where, when, why, or how for more specific answers.
6. Provide example responses
Include example output format so the model understands what you expect.
"great pen" => Positive
"I hate when my phone dies" => Negative
[insert post] =>
7. Break up complex tasks
- Divide into subtasks - Split into multiple prompts if results aren't reliable.
- Ask for confirmation - Check if the model understood your instruction.
- Think step by step - Ask the model to reason through the problem systematically.
8. Experiment and be creative
Try different prompts, determine what works, and adjust accordingly.
Evaluate model responses
Review responses to ensure quality. Make changes as needed, you can even ask one model to check output from another. Prompt engineering is an iterative skill that improves with practice.

