User Permissions and Access
What is AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) securely manages identities and access to AWS services. By default, all actions are denied - you must explicitly grant permission.
IAM follows the Principle of Least Privilege: only give people and systems access to what they need. It provides users, groups, roles, and policies to configure access based on your security needs.
User Permissions and Access Video
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our learners.
IAM Identities
Root User
The account owner created when you first start an AWS account with full permissions. Best practices:
- Use a strong password and enable MFA
- Avoid using root user for daily tasks
- Create IAM identities for daily work
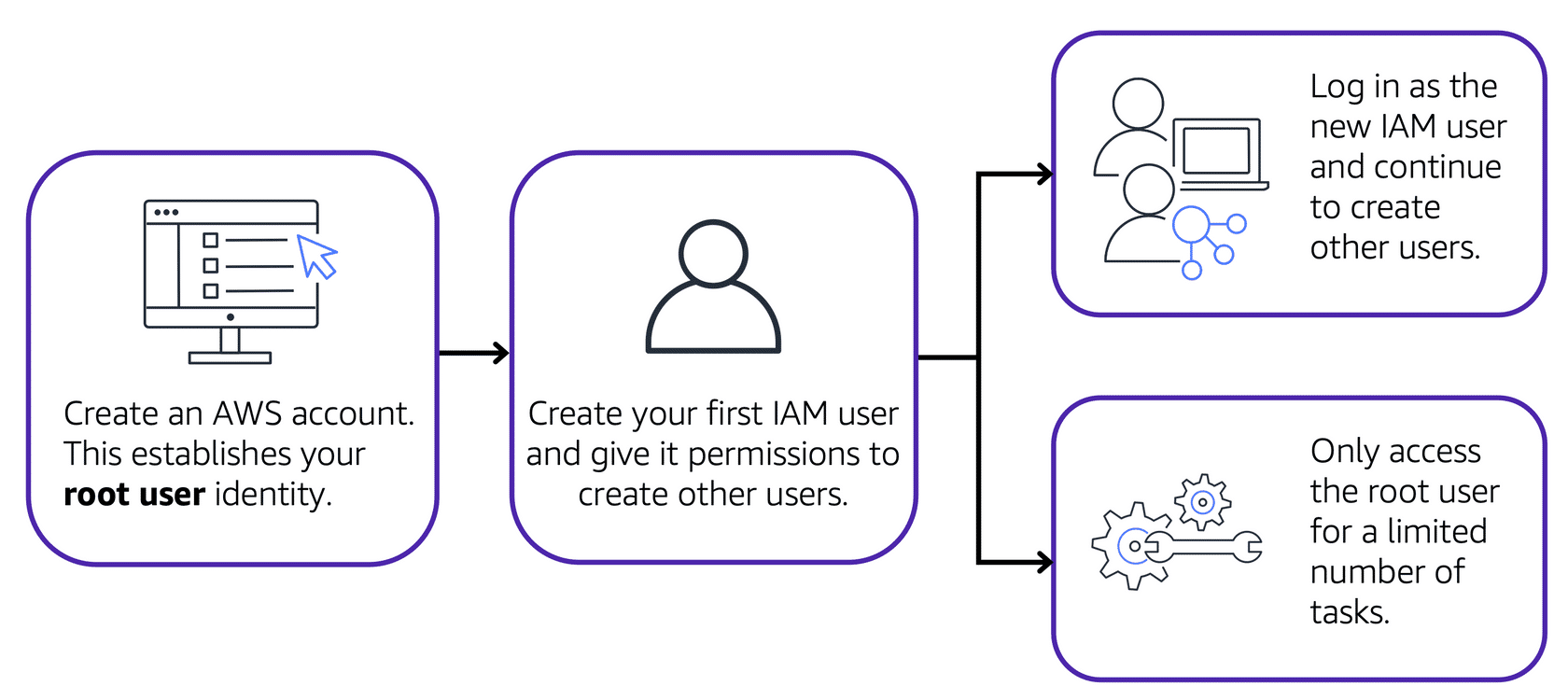
Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Users
Represents a person or application that interacts with AWS. Created without permissions by default - create one IAM user per individual.
IAM Policies
Documents that allow or deny permissions to AWS resources. Customize access for each user based on what they need.

Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Groups
A collection of IAM users. Policies assigned to a group apply to all users in that group.
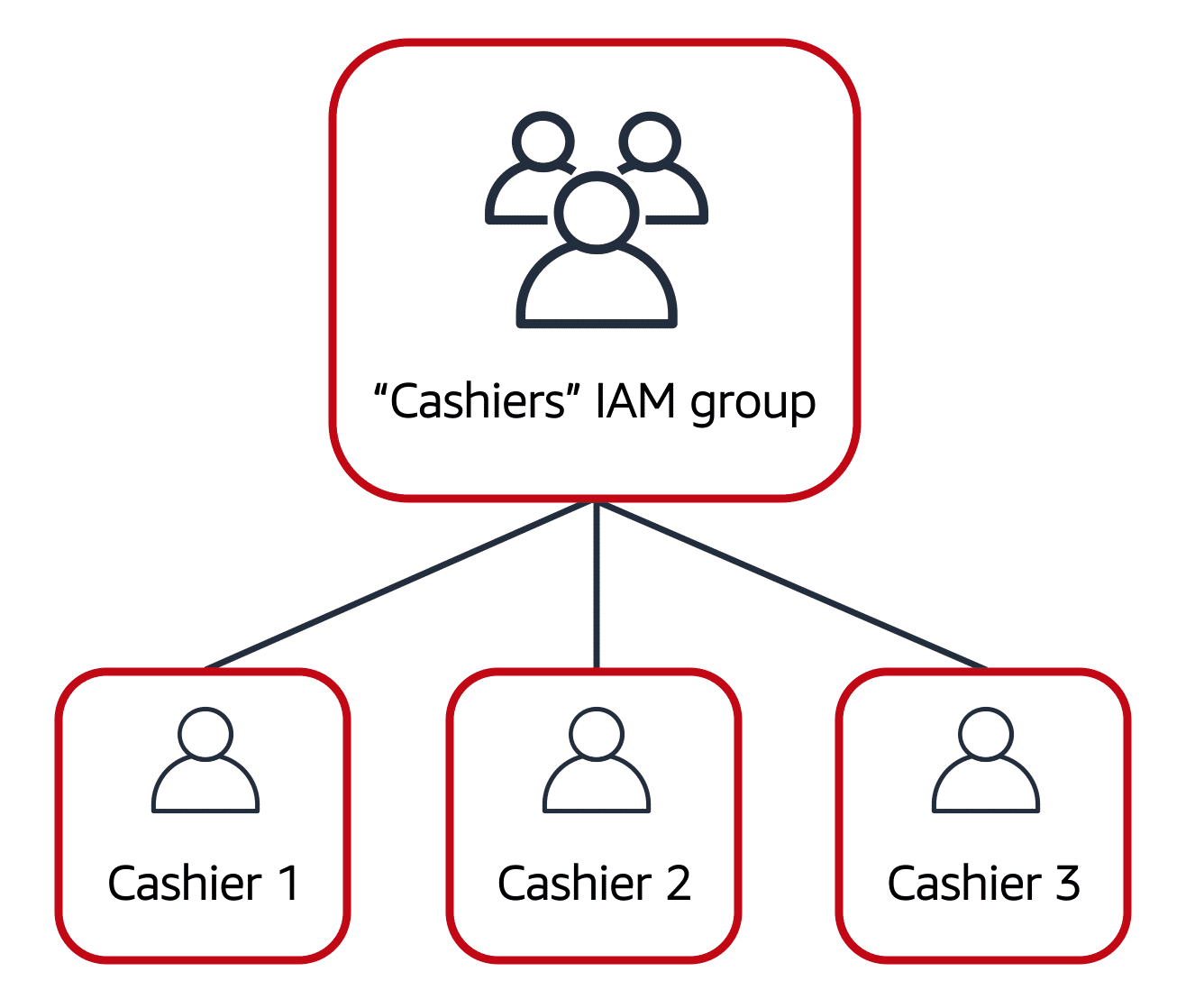
Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Roles
An identity you can assume to gain temporary access to permissions. When assuming a role, you abandon previous permissions and take on the role's permissions. Best for temporary access scenarios.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Requires at least two verification methods to log in, providing an extra security layer. Can use security codes sent to mobile devices or email.
Additional Services
| Service | What It Does |
|---|---|
| IAM Identity Center | Centralizes identity management and single sign-on across AWS accounts |
| AWS Secrets Manager | Securely manage and rotate credentials, API keys, and secrets |
| AWS Systems Manager | Centralized view of nodes with automated patching and management |

