AWS EBS - Elastic Block Store
What is AWS EBS?
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides persistent block-level storage volumes for EC2 instances. Unlike instance stores, EBS data persists even when the instance is stopped or terminated.
Common use cases are: database hosting, application backups, rapid deployment of dev environments.
EBS Benefits
- Data persistence: Data remains available even if the EC2 instance stops
- Migration: Move volumes between Availability Zones using snapshots
- Flexibility: Attach volumes to different instance types, modify size and performance on the fly
- Disaster recovery: Snapshots provide reliable backups across regions
EBS Snapshots
What are Snapshots?
EBS snapshots are incremental backups. The first backup copies all data; subsequent backups only copy changed blocks, saving storage costs.
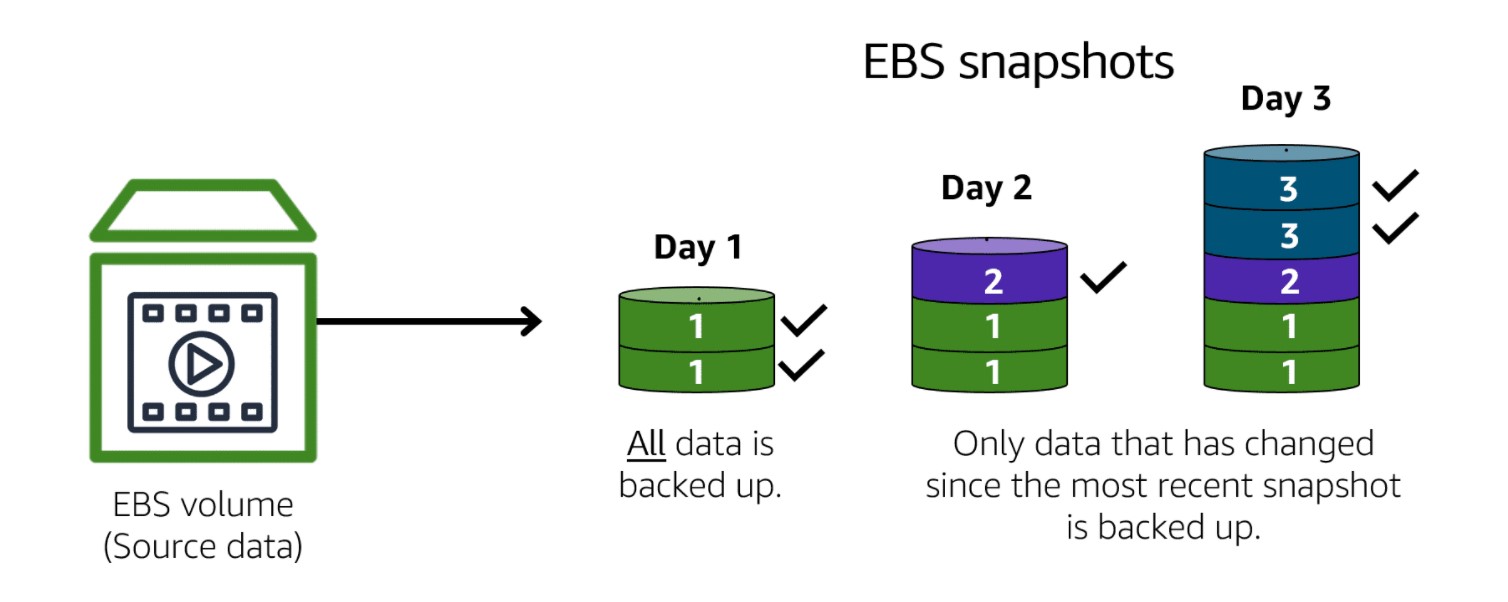
Image created by Amazon Web Services
Snapshots are stored redundantly across multiple Availability Zones using Amazon S3. When you delete a snapshot, only data unique to that snapshot is removed.
Data Lifecycle Manager
Automate snapshot creation, retention, and deletion. Schedule backups during off-peak hours and automatically delete outdated ones to control costs.

