AWS Cloud Global Networking
Global Networking
AWS provides services to route users to your applications quickly and reliably, regardless of where they are in the world.
Global Networking Video
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our learners.
Domain Name System (DNS)
DNS acts like a phone book for the internet, connecting domain names (like w3schools.com) to IP addresses. It's how users find and access your website.
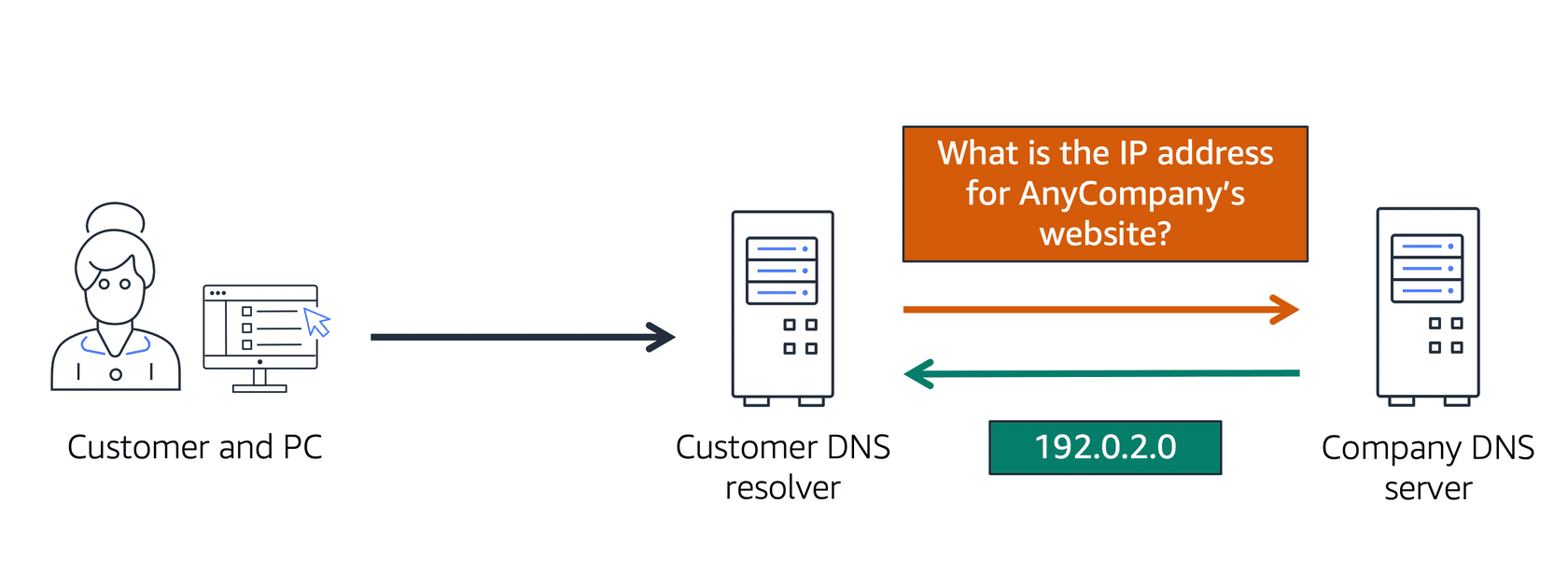
Image created by Amazon Web Services
AWS Networking Services
Amazon Route 53
Route 53 is AWS's DNS web service that routes users to your applications running on EC2, load balancers, or even infrastructure outside AWS. You can register new domains, transfer existing ones, and manage all DNS records in one place.
Route 53 + CloudFront Architecture
Route 53 and CloudFront work together to deliver content efficiently:
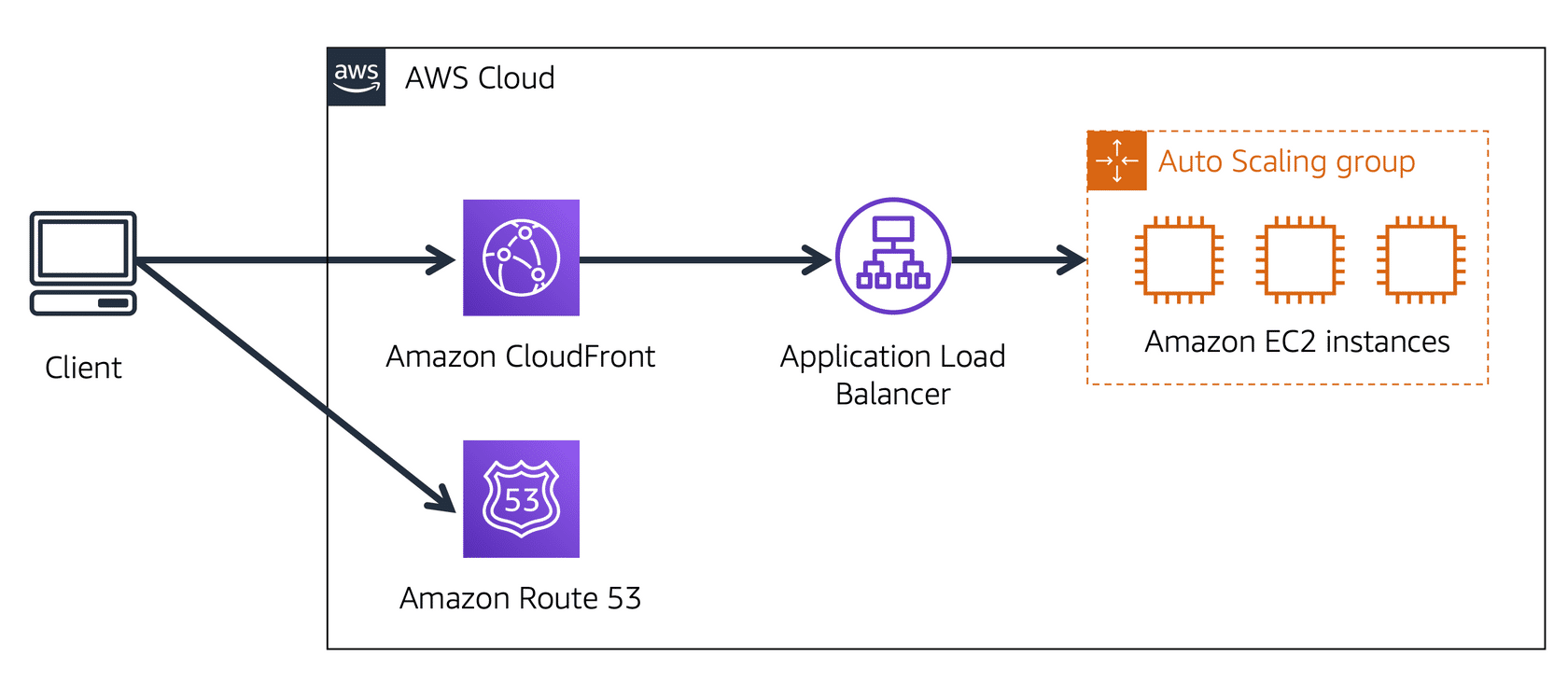
Image created by Amazon Web Services
- User requests data from the application
- Route 53 resolves the domain to an IP address
- The request goes to the nearest CloudFront Edge Location
- CloudFront connects to the Application Load Balancer
- The Application Load Balancer forwards the request to an EC2 instance
- A response is returned to the user
AWS Global Accelerator
Global Accelerator routes traffic through the AWS private global network instead of the public internet, improving speed and reliability. It provides intelligent routing and automatic failover.
Use cases: Gaming (reduced lag), financial services (reliable access during peak times).
Edge Services Summary
- Route 53: Scalable cloud DNS service
- CloudFront: CDN for low-latency content delivery
- Global Accelerator: Routes traffic through AWS's private network for better performance

